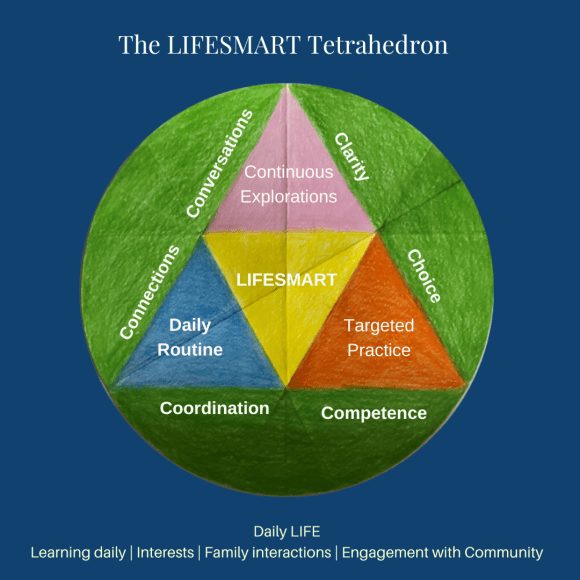
In this blog post, I want to clarify how to use the four LIFE pillars to think about your choices.
LIFESMART Tip: Enrich parent-child interactions (F: Family interactions) to set the stage for daily Learning (L).
Last week, I introduced three key techniques:
1) Regulation-Challenge-Reorganization (RCR),
2) Just Noticeable Differences (JNDS).
3) four patterns of interaction,
When a parent practices the three techniques consistently, parent-child interactions (F: Family interactions) improve setting the stage for daily Learning (L).
In this article, I will discuss the first technique, RCR practice by parents and daily Learning. I will also introduce the notion of co-regulation and explain how RCR is a key tool for practicing co-regulation.
Choosing your Path
If you are a parent of a young child and are wondering where to begin, I invite you to consider the idea of co-regulation. Co-regulation is the foundation of learning. Yet, it does not seem to be identified as a good starting point for parents of neurodivergent children! We were fortunate to discover co-regulation through Relationship Development Intervention (RDI).

The Journey Begins
Initially, we focused on L (Learning daily) and F (Family interactions).
In the early stages, Relationship Development Intervention (RDI) emphasizes the interplay of these two elements. Under typical development, parent-child interactions are the foundation for learning. At this stage, we did not address I (Interests) or E (Engagement with community) explicitly.
The key point is that while all LIFE components are equally important, we may focus more on different elements at different times.
The focus of RDI was the guided participation relationship between the parent and child. Restore the Family interactions (F) to build the foundations of guided participation which is the base for Learning daily (L).
The focus of Family interactions in the early years is developing parent and child interactions. Neurotypical development also begins here. Dr. Gutstein used to say that neurotypical children have thousands of hours or co-regulation practice with parents before they start peer interactions. If co-regulation with parent is disrupted, that needs to be restored before trying to get peer interactions.
Co-regulation and Daily Learning
Read about co-regulation here.
According to this article, “The supportive process between caring adults and children, youth or young adults that fosters self-regulation development is called “co-regulation.”
Role of parents/caregivers
- Provide a warm, responsive relationship
- displaying care and affection;
- recognize and respond to cues that signal needs and wants
- provide caring support in times of stress
- Create an environment that is physically and emotionally safe for children, youth, and young adults to
explore and learn at their level of development .- Develop consistent, predictable routines and expectations
- Provide clear goals for behavior regulation
- Provide well-defined logical consequences for negative behaviors.
- Teach self-regulation skills
How does Regulation, Challenge, Reorganization (RCR) enhance co-regulation and daily learning?
The four patterns of activities discussed below are based on RCR (Regulation, Challenge, Reorganization) is one of the most valuable parenting concepts that I learned from Relationship Development Intervention (RDI). The parent sets up a pattern of interaction with competent roles for parent and child. The key is to set up a predictable pattern the child can recognize so that the child is regulated in the activity. Once the child is familiar with the pattern, introduce variations or challenges. Add the variations gradually to enable the child to accept the variations and reorganize the initial pattern of interaction. Practice the basic pattern for many days before introducing variations. This article describes four simple patterns of interactions that parents can use to implement RCR in daily life activities.
RCR reduces stress and enhances engagement by providing predictability, incremental development, and consistency.
RCR is a technique for creating consistent, predictable interactions while introducing variations and novelty. RCR is a technique for practicing co-regulation.
Learn more about RDI here.
Watch the video below for a description of how RDI changed our path: